Services (default)
Overview#
Services are a work in progress. As we are still in the progress of creating a non-ui maintained service, this usage may change.
Example#
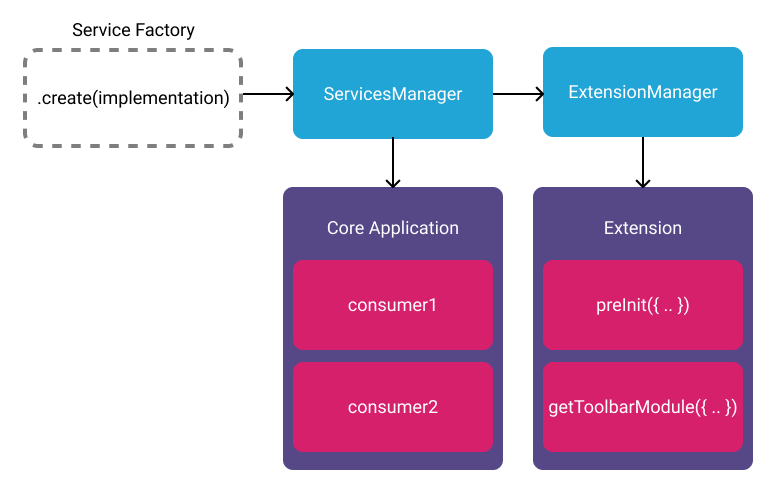
The simplest service return a new object that has a name property, and
methods/properties that give the service its functionality. The "Factory
Function" that creates the service is provided with the implementation (this is
slightly different for UI Services).
const _speak = () => { console.warn('Speak is not implemented');};
/** * Factory function to create `HelloWorldService` * * @param {object} implementation * @param {function} implementation.speak - Speak's implementation * @returns HelloWorldService */export default function createHelloWorldService({ speak }) { return { name: 'HelloWorldService', speak: speak || _speak, };}A service, once created, can be registered with the ServicesManager to make it
accessible to extensions. Similarly, the application code can access named
services from the ServicesManager.
// In the applicationconst speak = () => { window.alert('HELLO WORLD');};const HelloWorldService = createHelloWorldService({ speak });const servicesManager = new ServicesManager();
servicesManager.registerService(HelloWorldService);
// In an extensionconst { HelloWorldService } = servicesManager.services;
if (HelloWorldService) { HelloWorldService.speak();}